Melting Point of Syn and Anti Addition
This article will use cycloalkenes as examples. The melting point was 199-203C and the NMR J values angle is at 167 which both prove the erythro-23-dibromo-3-phenylpropanoic.
What Is The Difference Between Syn And Anti Addition In Organic Chemistry Quora
Syn addition is the addition of two substituents to the same side of the unsaturated molecule.
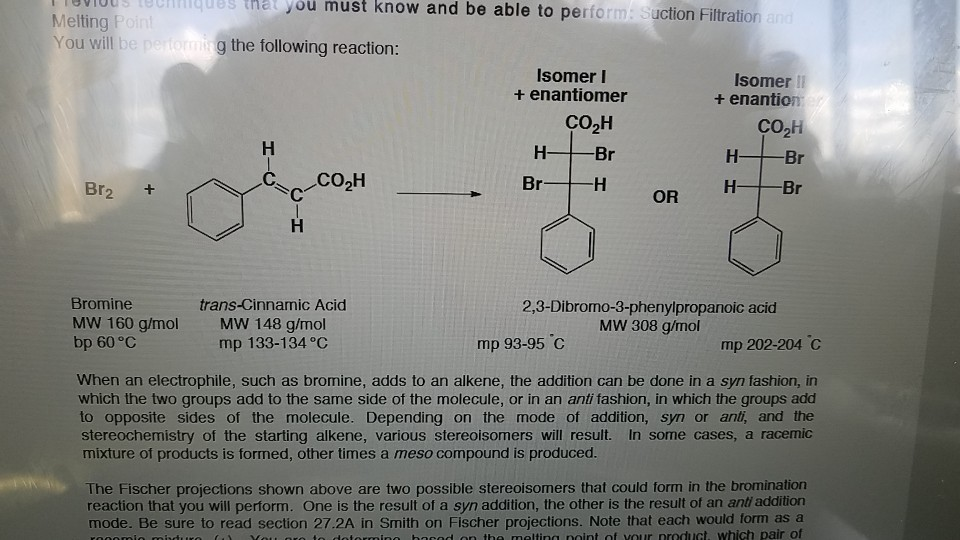
. This experiment is very reproducible and was performed with students of the first year of the Chemistry degree. View Entire Sample Download Sample Text preview In this experiment the stereochemistry of 23-dibromo-3-phenylpropanoic was found to determine syn or anti addition of bromines. The theoretical melting point range was 2034-2056 o C 2027-2053 o C therefore telling that the product formed was erythro-23-dibromo-3-phenylpropanoic acid since the melting point values recovered was close to 202-204C value.
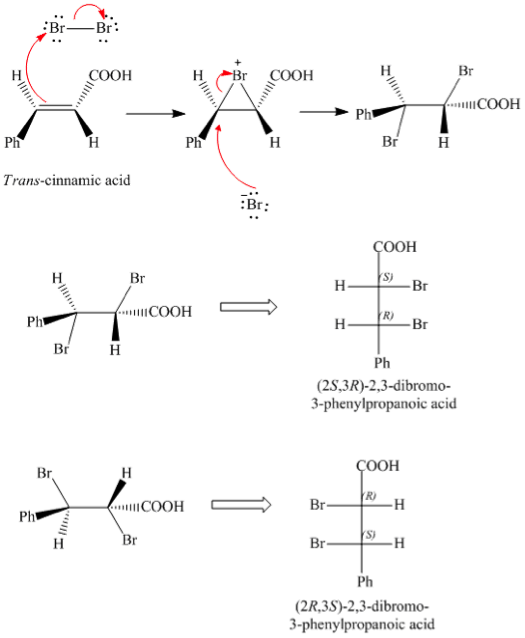
Because the melting points of erythro- and threo- dibromides differ by more than 100 deg C the product can be easily identified by its melting point. The product that was obtained is 2S3R-23-dibromo-3-phenyl propanoic acid and the identity of the product can be confirmed through the melting range. In the case of a asymmetrical alkene any type of addition will result in enantiomers and hence a racemic mixture.
Acid only adds by syn-addition only adds by anti-addition or if both products are produced. Accomplish this goal I carried out the bromination of trans-cinnamic acid in order to determine the. From this information you should be able to conclude whether the reaction proceeded by syn or anti.
A mixture of both products would melt over. You are to determine based on the melting point of your product which pair of enantiomers is produced. Explain how this observation about the bromine addition to trans-cinnamic acid products supports either a.
Determination of the Stereochemistry of 23-dibromo-3-phenylpropanoic acid. Furthermore it eliminated the possibility of the product being a syn-addition product 95. Which would correspond to 2R2S and 2S3R 23-dibromo-3-phenylpropanoic acid mp 202-204 C but we are trying to determine whether this is a syn or an anti addition.
If the melting point is around 200-205C then the addition occurred via syn-addition. A majority anti-addition or c. You should show that syn andor anti addition leads to a 5050 mixture of enantio mers.
There are three possible types of mixtures here such as syn as the major product and anti as the minor etc. Stereochemical structure of the dibromide intermediate and find. Describe the melting range for each scenario Is the melting point you recorded consistent with one particular stereoisomer of the.
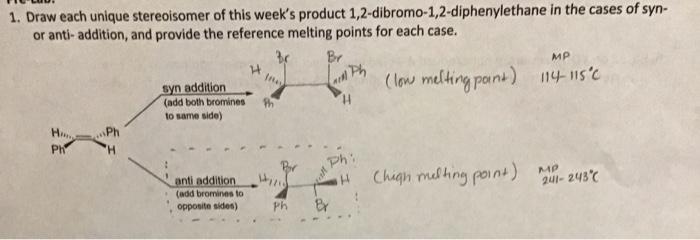
Note that each would form as a racemic mixture. Syn addition is the addition of two substituents to the same side or face of a double bond or triple bond resulting in a decrease in bond orderbut an increase. Anti adding components to opposite sides of the CC double bond.
Syn addition and the other is the result of an anti addition mode. Anti vs syn addition. Since there is no plane or point of symmetry a Meso compound can not be formed For a symmetrical alkene where.
The melting point of your product should enable you to determine whether the product is a racemic mixture of the erythro or the threo stereoisomers or a mixture of diastereomers. These addition reactions alter the bond order of the reactant molecule as well as the number of. In the case that there is a mixture of both products the melting range can be expected to be an average of the syn and anti periplanar melting ranges therefore 147-149.
See the answer Melting point range was 1734-1900 degrees celsius. If the melting point is around 93-95C then the addition occurred via syn. In this experiment the stereochemistry of 23-dibromo-3-phenylpropanoic was found to determine syn or anti addition of bromines.
In organic chemistry syn and anti addition are different ways in which two substituents can be added to a double bond or triple bond. Note that each would form as a racemic mixture. Describe the melting point you expect to observe if the isolated product is the mixture of both syn and anti addition of bromine.
Addition of chlorine is less Stereoselective than bromine addition. Write a This problem has been solved. The reason for such a high yield was due to substance not being fully dried when weighing most likely.
The melting range that was obtained was from 199- 201 C which is very close to the melting range of the anti-addition product 202-204 C. Answer 1 of 2. One session of 2 h is enough to perform the entire experiment which can also be conducted in a lower scale.
This is the main difference between syn and anti addition. You are to determine based on the melting point of your product whether one of the pairs of enantiomers is produced or if there is a 11 mixture of the two. Because of higher Electronegativity and smaller size of chlorine as compared to bromine.
A majority syn-addition b. If the melting point is around 93-95C then the addition occurred via anti-addition. Anti-addition mechanism yields erythron-23-dibromo-3-phenylpropanic acid syn addition yields threo-23-dibromo-3- phenylpropanoic acid and non-stereoselective mechanism which yields a mixture of both erythro and theo products.
An equal mixture of both syn- and anti-addition. Answer 1 of 3. Anti addition on the other hand is the addition of two substituents in opposite directions.
The melting point. For an anti periplanar product the melting range is expected to be from 202-204 degrees Celsius. In the case that the product is syn periplanar the melting range is expected to be 935-950 degrees Celsius.
D We are able to determine how the addition occurred based on melting point as diastereomers possess different melting points. By knowing which enantiomeric pair is formed one can predict a plausible mechanism. The product will be purified using recrystallization and the melting point will be identified.
The melting point was 199-203C and the NMR J values angle is at 167 which both prove the erythro-23-dibromo-3-phenylpropanoic. We determined our melting point to be 199 C. Here reaction proceeds via intermediate formation of an equilibrium.
One is the result of a syn addition the other is the result of an anti addition mode. Brominetrans-Cinnamic Acid23-Dibromo-3-phenylpropanoic acid MW 160 gmolMW 148 gmolMW 308 gmol bp 60 Cmp 133-134 Cmp 93-95 Cmp 202-204 C When an electrophile such as bromine adds to an alkene the addition can be done in a syn fashion in which the two groups add to the same side of the molecule or in an anti fashion in which the.
Solved Based On The Results What Product Would You Expect Chegg Com
Solved Draw The Overall Reaction Including Stereochemistry Chegg Com
What Is The Difference Between Syn And Anti Addition In Organic Chemistry Quora
No comments for "Melting Point of Syn and Anti Addition"
Post a Comment